Final Exam Review Sheet 2024
CLCS 383 TAKE HOME FINAL EXAM WILL BE POSTED IN
BRIGHTSPACE AS AN ATTACHED FILE BY WED., APRIL 24. RETURN IT WITH YOUR NAME CLEARLY
STATED TO rauhn@purdue.edu AS AN ATTACHED
FILE BY FRIDAY, MAY 3
Final Exam Map:
FILL IN THE BLANK Items:
Vespasian (the Flavians), Trajan
(the Antonines), Trajan’s Column, Hadrian, the
Pantheon, Imperial Fora, Dacia, Masada, Jewish Rebellions, the
Limes, Colosseum, Nero’s Golden House, Roman Roads, Aqueduct, Basilica,
Council House, meretrix, marriage and gender relations, Petronius, the Satyricon, Encolpius, Trimalchio,
slavery, Stoics, Epicureans, Cynics, Gospel of John, Mystery Cults, Ancestor
Cults, Hero Cults, Hubris, Olympic and Chthonic Deities, Ritual, Sacrifice,
Divination, Nous, Logos, Boule kai Demos; Imperial
priests, Oikoumene; Barracks
Emperors, Septimius Severus, Diocletian,
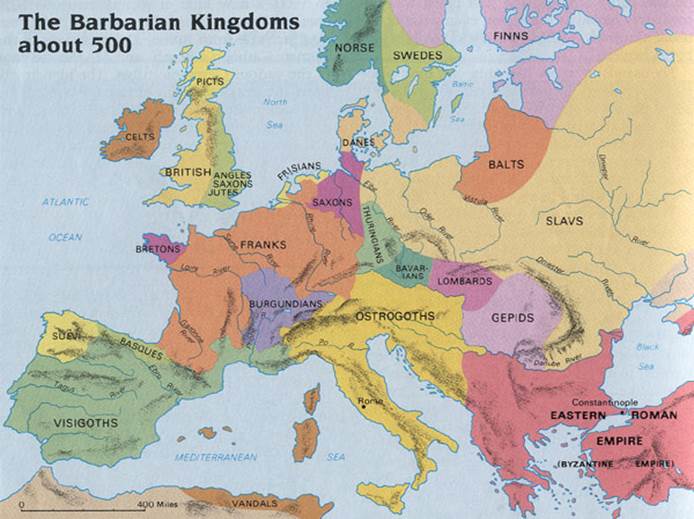
Constantine, Munera, Diocese, Visigoths, Vandals, Franks, Huns,
Stilicho/Odoacer, Edict of
Milan, Arianism, Donatism,
Council Of Nicea, Helena, Constantinopolis,
Council of Nicea
312 AD, Justinian, Vicarii, Foederati, dediticii, hospitalitas,
Visigoths (Alaric), Vandals, Franks (Clovis I), Huns (Atilla), Stilicho /
Odoacer, Edict of Milan, Edict of Toleration Arianism, Council
of Nicea,
Constantinopole, Ambrose,
Jerome, Augustine, Petrine Theory (of Apostolic
Succession),
Justinian and the Reconquest
SHORT ESSAYS:
GENDER RELATIONS IN THE
ROMAN EMPIRE: Discuss evolving gender relations in the
early Roman Empire. How did the status
of Roman women change? What new models
for women's behavior presented themselves?
Discuss evidence of increasing opportunities for women in mainstream
society and why. Support your discussion with evidence from Petronius and / or
Juvenal’s Satires.
Boule kai Demos: Discuss the role of the local city councils in the
administration of the Roman Empire. Include mention of Dekaprotoi,
Eirenarchs, and Imperial Priests. What were the
avenues for upward mobility for non-Roman, non-Italian elements.
MILITARY DEVELOPMENTS IN THE AGE OF
THE BARRACKS EMPERORS (235-284 A.D.). Discuss generally
military trends and technical adaptions during this period of internal civil
war and increasing barbarian pressure on the frontiers.
THE FALL OF THE
ROMAN EMPIRE (The
Four Reasons Are Found Here – scroll down to Later Roman Empire, Crisis and Collapse (234-476 AD)
Discuss four reasons for
the collapse of the imperial system, 220-476 A.D. How did each of
the following influenced the decline: 1. Constantine, 2. Munera, 3. Vandals, 4. Vicarii.
IMAGE IDENTIFICATION – I may use images as prompts
for the fill in blank and short answer questions.
You are responsible for the labeled images
in the powerpoints listed below and the following:
(23.29 MB)
(171.13 MB)
(22.41 MB)
(15.52 MB)
(3.62 MB)
(839.35 KB)
(12.1 MB)
(482.25 KB)
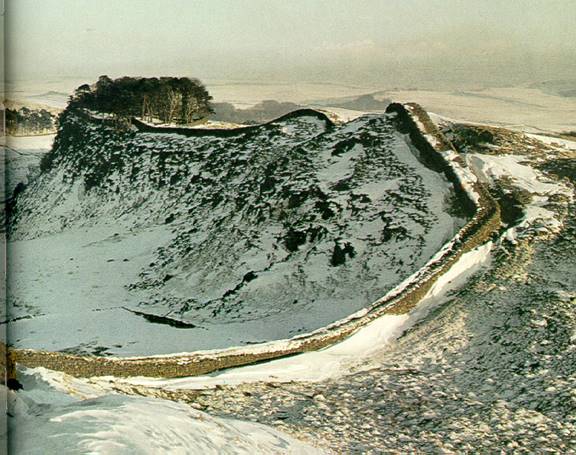

Hadrian’s
Wall

Roman Wall
Painting at Pompeii: symptomatic of Roman Baroque Art employing “tromp d’oeil” perspective of an open window looking out toward
abstract architectural theater elements
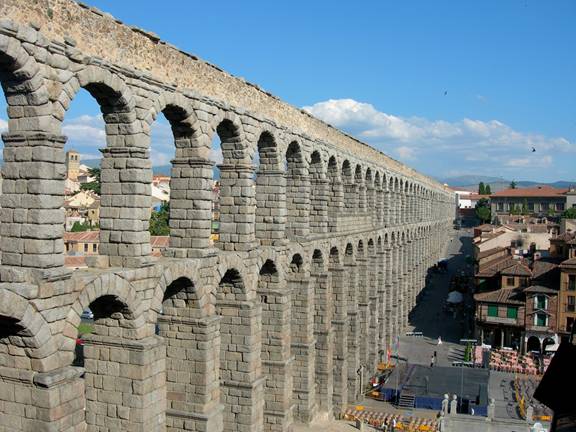

Roman
Aqueduct in Segovia Spain: good example of Roman Engineering and Reliance on
vaulted arches.

The Walls of
Theodosius (390 AD) at Constantinople, moat and triple line of walls that
extended from the Golden Horn to the Sea of Marmara, protecting the urban
settlement from foreign assault until 1453 AD.

The Golden
Gate at Constantinople; its remodeled doorway serving as a metaphor for the
decline of the Roman World.

Haghia Sophia, the Church of Holy Wisdom constructed by the Emperor Justinian (527-565 AD) in Constantinople. Until
modern times, the tallest domed structure in the world.